Tensorflow
Introduction to Tensorflow
- Tensorflow Modules and APIs
- Python, C++, Go, Java supported
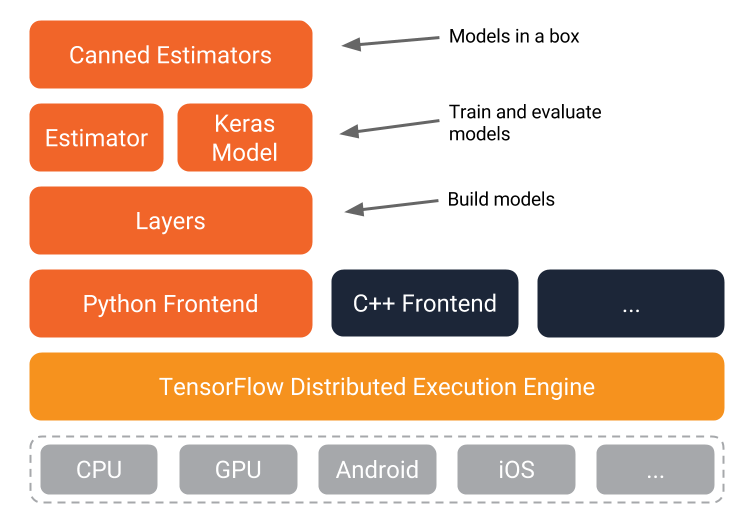
- Python, C++, Go, Java supported
- a declarative language (vs. imperative)
- use functions to express mathematical modules, use functions as computation units
- a graph-based computation model
Deep Learning Applications
- Internet
- autorecommendation (ad, music)
- OCR
- photo labels
- Machine Translation
- Face Recognition
- Scientific Research
- patten recognition (eg. astronomy)
- System Engineering
- auto parameter tuning
- Agriculture
- cow and pig
- medical and clinic
Basics
Graph
- Tensorflow create a default graph after importing, all operations will go there by default
- tf.get_default_graph()
- You can create own graph and get operations there
g = tf.Graph() with g.as_default(): pass
- tf.rest_default_graph()
- edges
- tensors/sparse tensors
- nodes
- operations - computation
- variable - storage
- constant - placeholders
Session
- tf.session([target=], [graph=], [config=]) object encapsulates the environment in which tf.Operation objects are executed and tf.Tensor objects are evaluated
- target is execution engine, graph is data flow graph, config is start config
- sess.run(<graph>, [feed_dict])
- _tf.InteractiveSession() - _create a session, definitions follow
- <graph>.run() - run the graph
- with tf.Session() as sess:
- tf.global_variable_initilalizer().run
- or s.run(global vairbale initializer())
- <variable>.eval
- tf.global_variable_initilalizer().run
- 3 Steps when a session runs
- get tensors
- evaluate tensors - tensor.eval, operation.run
- run session - session.run
- Tensorflow will automatically execute sub-graphs in typological order and distribute computations in different devices(per cpu/gpu/tpu)
- nodes - can assign nodes to run on different devices
- with tf.device(<device>) - will run on a certain device
- client -server: the actual execution is the client sends the graph to the server (C++) and server distributes to workers
- nodes - can assign nodes to run on different devices
Tensor
Basic datatype is tensorflow
Inputs
- tf.placeholder(<tf datatype>, (shape))
- data type like tf.float32
- tf.Variable
- tf.get_variable(<name>, <shape=>, <dtype=>)
- is a special type of operations, returns a tensor
- tf.constant(<value>)
Operations
tf.
- @ - tf.matmul()
- Arithmetic
- add/multiply/mod/sin/sqrt/fft/argmin
- Aggregation
- reduce_mean(x, [dim])
- List
- size/rank/split/reverse/cast/one_hot/quantize
- Gradient
- clip_by_value, clip_by_norm, clip_by_global_norm
- Logical
- identity/logical_and/equal/less/is_finite/is_nan
- Dataflow
- enqueue/dequeue/size/take_gard/apply_grad
- Initialization
- zeros_initializer/random_normal_initializer/orthogonal_initializer
- Neural Network
- convolution/pool/bias_add/softmax/dropout/erosion2d
- nn
- loss functions
- activation functions
- sigmoid, softmax
- Layers
- dense
- Random
- random_normal/random_shuffle/multinomial/random_gamma
- String
- string_to_hash_bucket/reduce_join/substr/encode_base64
- Image
- encode_png/resize_images/rot90/rot90/hsv_to_rgb/adjust/gamma
<variable>.
- assign
- assign_add
Saver
Built-In Optimizers
tf.train
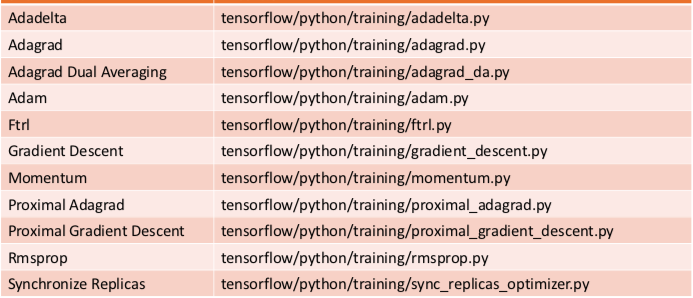
To use optimizers
- compute_gradients
- operations on gradients (eg. clip, weighted)
- apply_gradients: apply to variables
or, use optmizer.minimize(loss, global_step) directly
Keras
Provides higher level APIs then the Tensorflow. Support key functionalities to build neural networks fast, work together with Tensorflow
Common functions
model.
- add()
- add layers
- compile()
- fit()
- save()
model types
- model = Sequential()
layers
from keras import layers
- Dropout: applies dropout
- Dense: fully-connected layer.
- Flatten: flattens the input, does not affect the batch size.
- Activation: applies an activation function.
- LeakyReLU: applies leaky relu activation.
- Conv2D: convolution layer
- filters : number of output channels;
- kernel_size : an integer or tuple/list of 2 integers, specifying the width and height of the 2D convolution window;
- padding: padding="same" adds zero padding to the input, so that the output has the same width and height, padding='valid' performs convolution only in locations where kernel and the input fully overlap;
- activation: "relu", "tanh", etc.
- input_shape: shape of input.
- MaxPooling2D: performs 2D max pooling.
Utilities
Used for data processing
- to_categorical(y, num_classes= None, dtype='float32')